Remote Deployments with nixos-rebuild

In last week’s article, we got to know nixos-rebuild
a bit closer:
We’ve seen how it can be used to switch to a new system configuration, or only
test the new system configuration in a VM.
This week, we shift up a gear and look at nixos-rebuild’s remote building and
deploy capabilities.
As observed last week, nixos-rebuild provides functionality along two
different axes:
- Command Targets
- Just evaluate the NixOS configuration
- Just build it
- Activate the new NixOS config temporarily or permanently
- Dry-run activation to see the impact on the system
- Build and run a VM for testing
- Locality
- Local NixOS rebuilds
- Remote deployment to other hosts
- Remote building of the new NixOS configuration
This time, we have a close look at the locality axis!
Locality: How Do Remote Builds and Remote Deploys Work?
The parameter --build-host changes where the system is built:
The build host may be a faster machine or a machine with a completely different
architecture after all.
To deploy the system on a different one than the local one, use --target-host.
Now we have 3 systems: The machine that executes nixos-rebuild, the build
host, and the target host.
These can all be the same or individual systems.
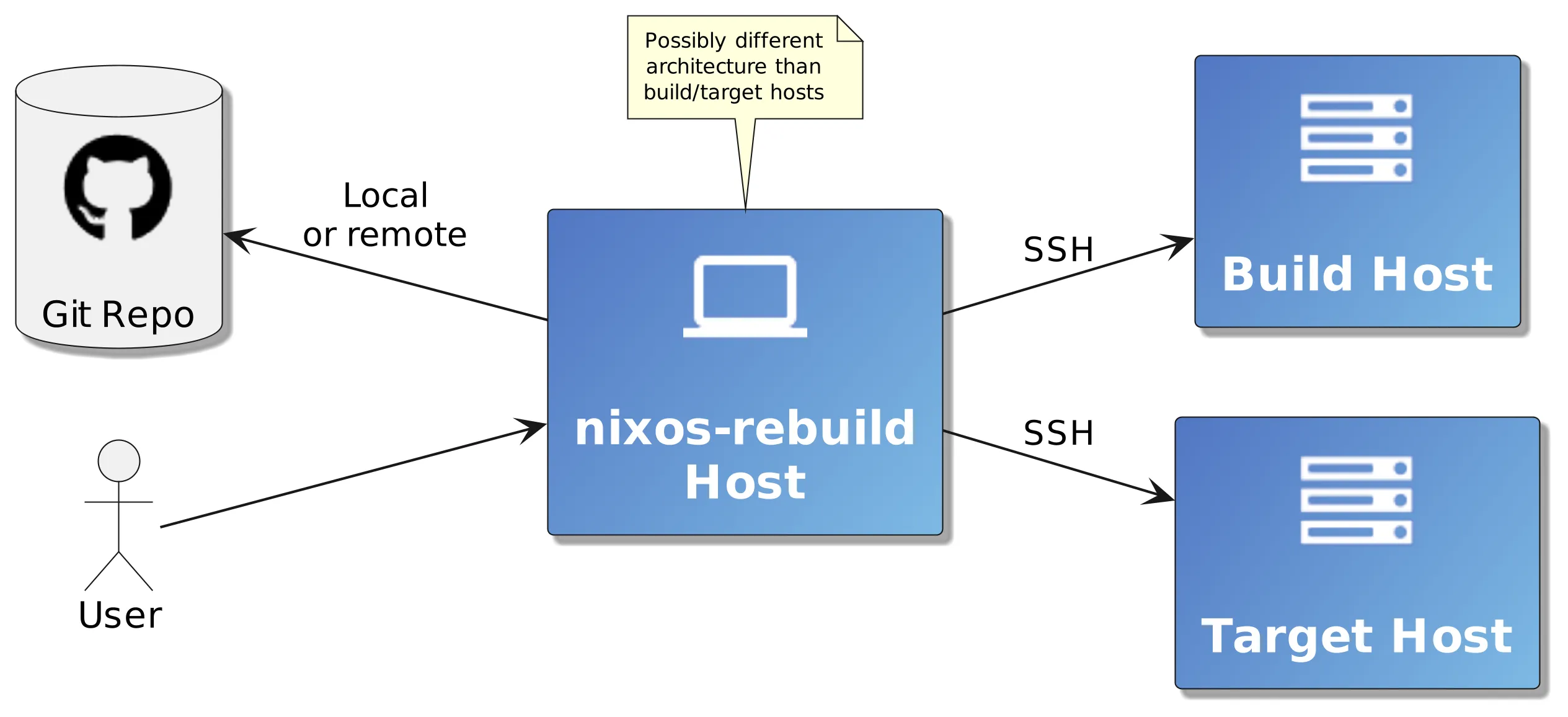
Let’s look at an example invocation:
nixos-rebuild \
--flake .#mySystem \
--build-host builduser@buildhost \
--target-host deployuser@deployhost \
--sudo \
switchPlease note that on macOS you also need to provide the
--fastflag.
The NixOS configuration selection happens in the --flake .#mySystem argument.
For this to work, the local flake.nix file (addressed by the .) must contain
an attribute like nixosConfigurations.mySystem.
On the target host deployhost, the user deployuser is used for
deployment.
As normal users can’t change the system configuration, we either have to use
root for login, or elevate deployuser’s rights to root rights using
sudo.
In the latter case, --use-remote-sudo uses sudo during deployment on the
target host.
Note that we would not prefix the
nixos-rebuildcommand withsudowhen deploying on a different host because we don’t need root rights on the local host for this.
The following sequence diagram illustrates what happens when we run this command:

nix build .#nixosConfigurations.mySystem.config.system.build.toplevel- Copy the result to the target host
nix-env -p /nix/var/nix/profiles/system --set <toplevel storepath>(on the target host)sudo <toplevel storepath>/bin/switch-to-configuration switch
toplevel is a special package that contains the switch-to-configuration
script, which activates a given system configuration on any NixOS system.
(See also NixOS documentation about toplevel)
We could copy it to random NixOS hosts and activate it there (but as it also
describes disk partitioning etc., it won’t work everywhere).
This is also often called “top-level closure” because, from this package, nix
can calculate the list of all nix store paths that belong to this system.
Step 3 is not strictly necessary for trying out a system, but it registers this system as a generation. When the bootloader selection is updated, this system needs to be registered like this.
Step 4 does the final configuration switch, with the same effect on the target
host as a normal sudo nixos-rebuild switch would have had on our local
system.
NixOS provides atomic upgrades: The old running system on the target host remains completely unchanged until step 4 is executed. If the switch-over to the new system configuration fails, it is always possible to switch back to the old system generation.
Summary
nixos-rebuild is not only very versatile in what it can build (see
last week’s article) but also where it builds and
deploys.
We have learned that we can freely choose where the NixOS system closure is
built, and where it deploys to.
This makes it very comfortable to also use slow/small machines for big
deployments, or to deploy to completely different architectures!
The feature set of nixos-rebuild is sufficient for most of the daily use
cases, but there are even more sophisticated tools out there, like
morph,
krops,
nixops,
nixiform,
colmena,
deploy-rs,
nixus,
bento,
Cachix Deploy, and
Hercules-CI Effects.



